
In contrast, electrolytes are chemical compounds that do disassociate into ions in water. Most nonelectrolytes are organic molecules - lipids, glucose, urea, creatinine, for example. Because of this, no electrically charged species are created when nonelectrolytes dissolve in water. Nonelectrolytes have bonds (usually covalent bonds) that prevent them from disassociating in a solution. It has been known that human plasma has a significantly longer shelf life than blood which is why it can be more sought after for those that need it as part of their treatment. In the image above, the ECF compartment is divisible in two compartments: (1) Plasma, the fluid portion of blood ( you may need to use this equipment to extract it from the other blood componants in a laboratory), and (2) interstitial fluid (IF), the fluid in the spaces between tissue cells. The ECF is the body’s internal environment and the cells external environment.Įxchange of gases, nutrients, water, and wastes between the three fluid compartments of the body. The remaining one-third of body water is outside cells, in the extracellular fluid compartment (ECF). The intracellular fluid is the fluid within the cells of the body. About two-thirds is in the intracellular fluid compartment (ICF).

There are two main fluid compartments water occupies in the body. So, the more muscles one has, the higher the total body water % will be.

In contrast, skeletal muscle contains 75% water. Adipose (fat) tissue is the least hydrated tissue in the body (20% hydrated), even bone contains more water than fat. This is because women typically have less skeletal muscle and more fat than males. The average young man is around 60% water, while a healthy young woman is about 50%. Total body water declines after infancy, and by the team one reaches old age, total body water is only about 45%.
BODY FLUID COMPARTMENTS POWERPOINT SKIN
Infants, with their low bone mass and low body fat, are 73% water! Due to the high concentration of water, an infants skin appears “dewy” and soft.
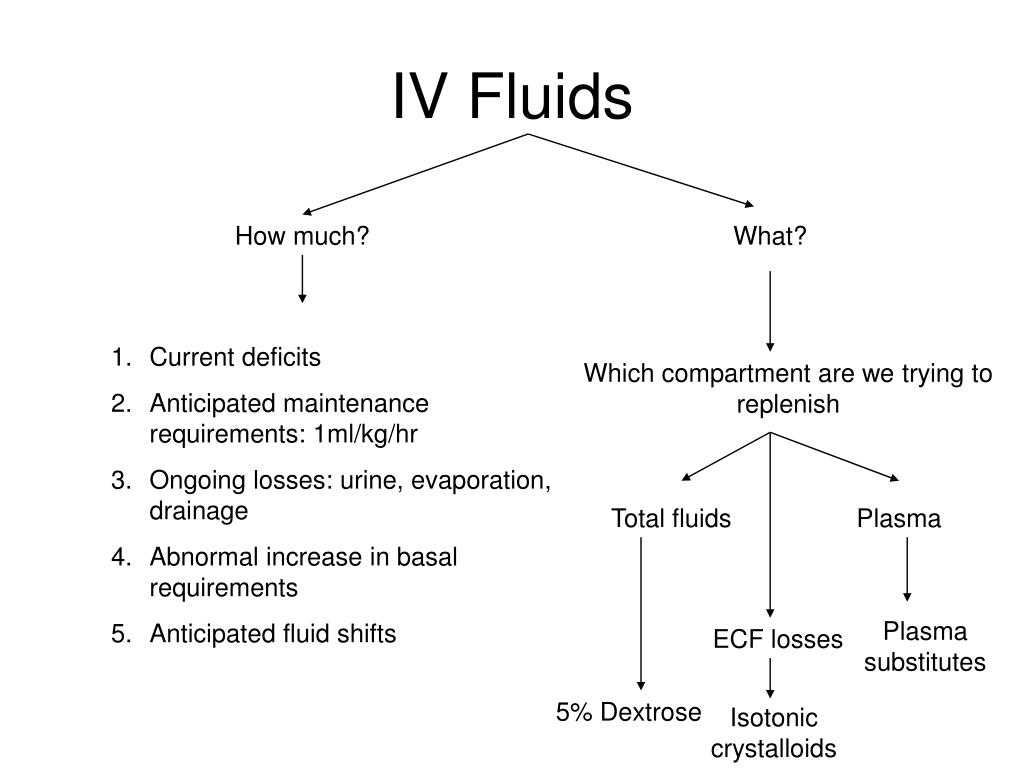
Factors which determine the overall water weight of a human being include sex, age, mass and body fat percentage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
